
There are two ways to answer that question, a short way and an extremely comprehensive way.
I’ll let the short answer come first; Google Tag Manager is an online tool provided by Google’s team to facilitate the integration of tracking codes and marketing tags on any website by marketers or data analysts without the need to wait for web developers.
The long answer, however, will require some reading. But, I promise at the end of this article, you will be in possession of a golden key to understanding user behavior on your website. You will also be able to take decisions based on truly actionable insights.
First, you need to know what is website analytics?

Let’s say that you have decided to become an online business owner and have your own e-commerce website developed. You have decided what products you will be selling at what prices and for which target segment. After starting for a couple of months, you realized that the products that you were expecting to sell, were the least performers.
Let’s say you have also started advertising your products for a specific country, but you wish to learn more about which cities within that country lead to the highest conversions in order to optimize your ad delivery.
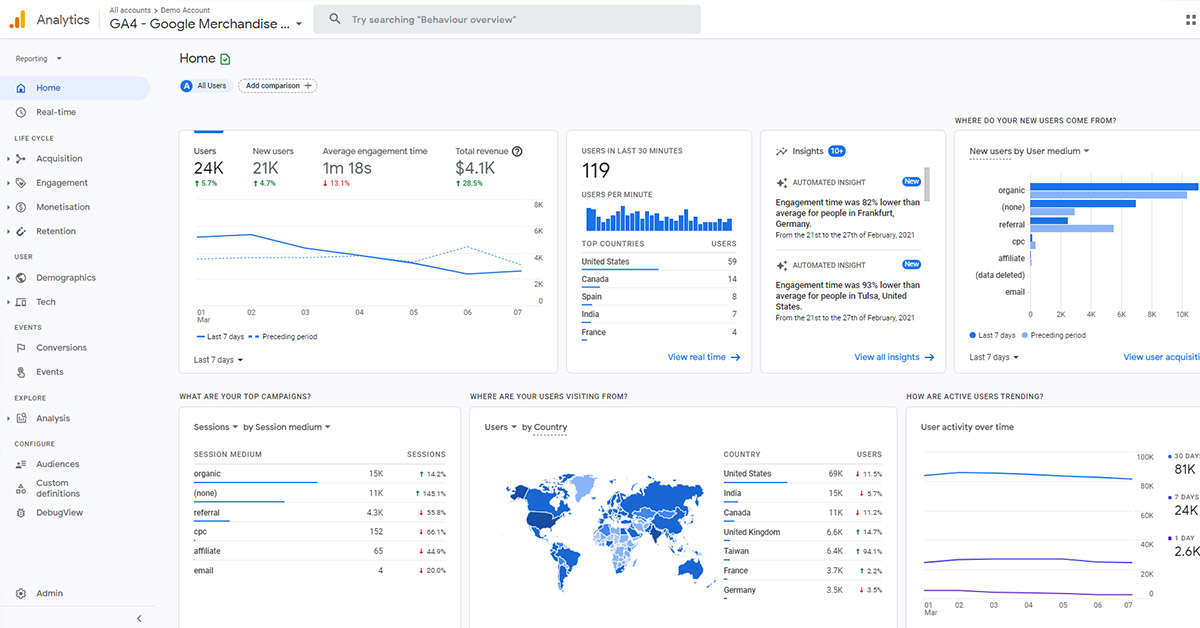
But how would you learn about all that if you can’t read more data about your website traffic and user performance? Lucky for you, Google has also provided a tool called Google Analytics, which is aimed to track, analyze and report that data for you.
Up to this point, you might have already been familiar with all the above, but you have certainly come here looking for the below!
How does Google Analytics read website data?
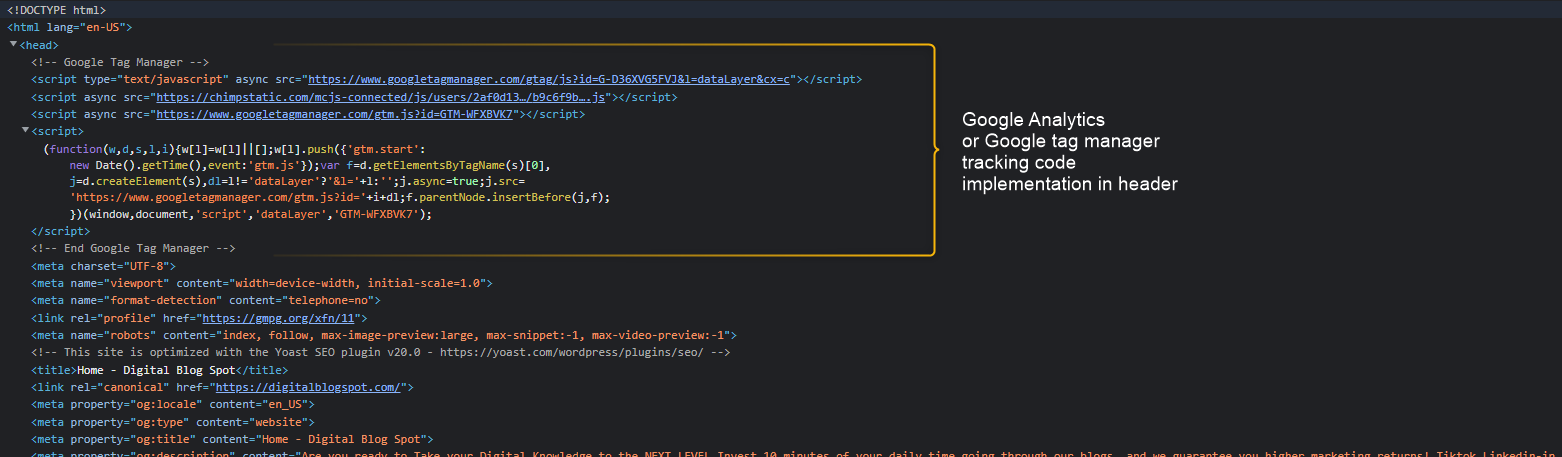
Google Analytics, is just a data analysis and reporting tool. But, in order to collect that data and transform it into readable information, it has to be integrated with your website by inserting Google Analytics tracking codes into the header and body sections of your website.
Previously, Marketers usually had to go grab a chair and sit right next to the web developer in order to provide him with the types of requested data to be sent to Google Analytics. Marketers and developers speak two different languages, however, and in most cases that process was pretty confusing and time-consuming.
Then, Google came up with the idea of developing a new tool to facilitate the process of integrating marketing tracking tags into the website without the need for a developer. That tool would be Google tag manager.
What are tracking tags (tracking codes)?

Tags are small snippets of code usually in HTML or JavaScript with a functional or a tracking objective
Functional Tags
Functional tags are code segments that are responsible to perform a specific action on your website. Those actions can be anything from showing a specific text on the screen, sending you to another page, or even submitting a form. They can even be responsible to help you check out a specific set of products.
Tracking Tags
Tracking tags are sets of tracking codes that come in two forms. The first type is cookies thrown on your browser to help collect data from the user’s browser and store them in third-party tools like Google analytics for reviewing and utilization. There is another type of tracking tag available which is our core in this article called “Pixels”. Those pixels are the type of tags responsible for sending user interaction reports to the analysis tools like Google Analytics.
How Google Tag Manager Works
In the past, developers used to integrate tracking codes by placing them directly in between the head and body tags of the original website codes.
Google Tag Manager Container Code

Now let’s take an example of how tag management works through Google Tag Manager. Imagine how a syringe works; you start by mixing all the medicines you need to insert into the human’s body in a separate container, then you inject the human body with the needle.
Google Tag Manager works the same way. First, you create a game container, then you start filling it with all the tracking codes you need for all your tracking tools like Google Analytics, and Meta Pixel. Afterward, you copy and paste the container code (needle) directly in between the website header and body tags of your source code.
Google Tag Manager Account Structure
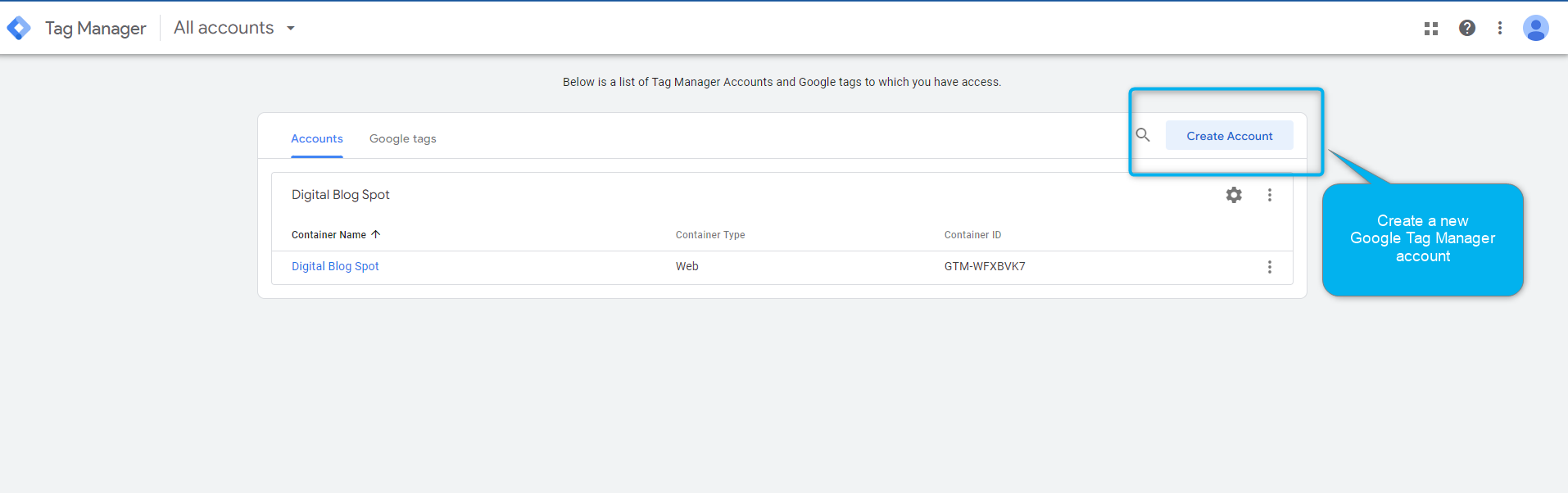
In order to start using Google Tag Manager, you will have to start by signing up for a new Google tag manager account. An account should include a group of containers for all your digital assets from your website, android app, IOS app, etc. And below are all the available Google tag manager container types
Google Tag Manager Container Types
Web Container: implemented by inserting tracking code directly between header and body tags
IOS Container: implemented through SDK integration
Android Container: implemented through SDK integration
AMP Container: implemented by inserting tracking code directly into the header and then working with JSON objects
Server Side Container: You will definitely need a developer for this one =)
Google Tag Manager container can be used to track user performance along multiple websites. So, for example, if you have two separate domains but you want to track the user journey through both websites, you can add the same container codes to the header and body tags of both websites’ source codes, and include a domain linker tag in your tag setup.
The three main parts (components) of any Google Tag Manager container
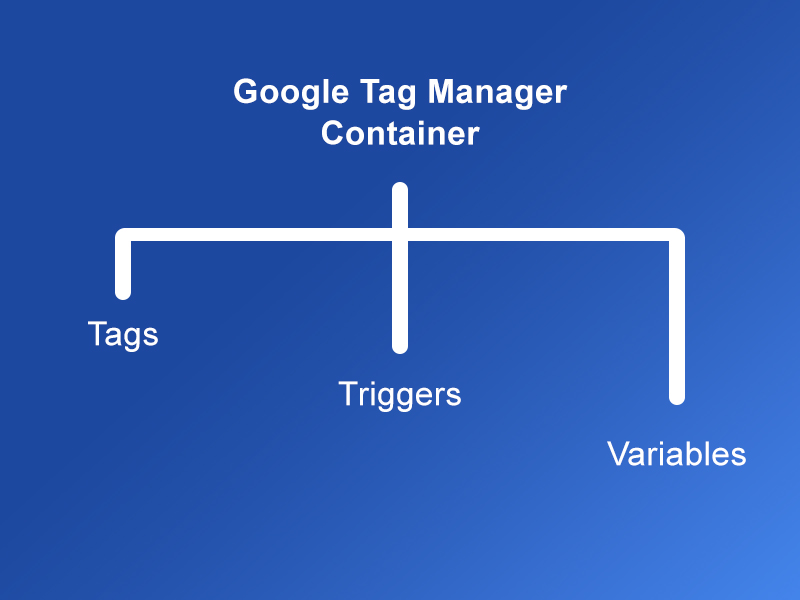
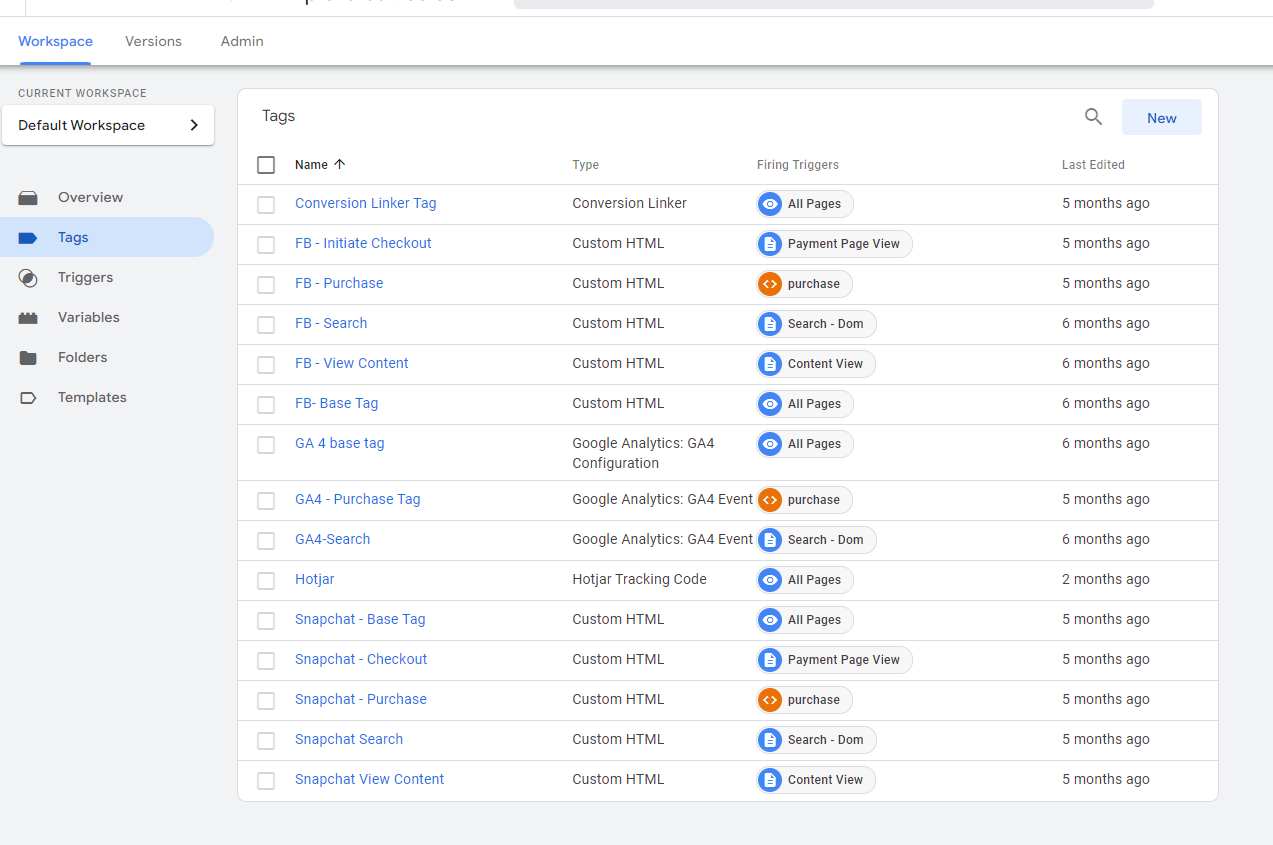
Tags
Tags are more like an electric current test lamp that lights whenever an action is taken, making you realize that someone clicked an on/off switch. Tags are the codes that load to tell google analytics that an action was taken on your website.
Triggers
Triggers are more like the switches placed on your electric circuit. Whenever a user hits a switch, a lamp lights and lets you know that someone has taken an action and hit that switch. Triggers can be anything from a page view, and button click, all the way to a specific time spent on a page.
Variables
If the lamp is controlled by two switches, a left one and a right one. When the left one is hit, the lamp lights in blue, and when the right one is hit, the lamp lights in yellow. Then the color of that lamp is the variable whose value is determined by the choice of switch.
An example of a tag manager variable can be anything from a product color, name, size, total purchase value, or currency. A variable’s value differs with each user’s interaction with your website.
Purchase event tracking example for an e-commerce website
In order to understand how the three elements work together to send data for third-party site analytics tools like Google Analytics or Meta pixel, we will have to take a live example.
Let’s take an e-commerce store selling T-shirts as an example in this scenario. The website goes live and traffic starts to flow in. Users start by landing on the home page and then checking some products, adding them to the cart and a few of them even check out and complete their purchase. Now you want to learn more about how many users went all the way through your conversion funnel until making a purchase. To do so, you will have to track the number of users who landed on the “thank you” page. You would even need to understand what products they purchased and how much they paid for their purchase.
Please understand that actions taken on your website are called events. And the process of tracking those actions on your website is called event tracking. For example, each page view on your website is considered an event, and each button clicked on your website is another event. By adding up those events, you can realize the volume of interaction on your website.
Back to our example. For you to learn when someone makes a purchase event on your website, you would have to use the three elements “Tags, Triggers, and Variables” in the following sequence.
When the user lands on the “thank you” page, a web page loads in his browser with the path “/thank-you”. When the web page is done loading, a trigger shall fire deploying the purchase event tracking tag. The tag, which works like a lamp, then tells Google Tag Manager that a purchase event tag was fired. Google tag manager then sends that information to Google Analytics for analysis.
There is one extra point to consider here; each time a purchase event happens, the products bought are different and the total value of each purchase is different from one user to another. That’s when variables come into play. Variables are the way to tell google tag manager the different values of each purchase done on the website. This is done by giving each aspect of the purchase a unique identifier on Google Tag Manager; for example, the products listed on the website will be given a “product-id” and that will be unique for each product. When a trigger is fired and an event tag is deployed, the product ID received by Google Tag Manager will be different from one event to another.
What are the benefits of using Google Tag Manager?
Using Google Tag Manager to manage your marketing tags has a lot of benefits for both marketers and website users alike.
Site speed

If you have an idea regarding the average number of tags an e-commerce website has to load before showing the final page structure for a user, you would be surprised at how slow they could be.
As you have previously learned, tracking codes are mostly placed in the header section of any given page. An e-commerce website, for example, might use a meta-pixel tracking code composed of base tags and standard event tags. In addition, almost every website needs, google analytics and google ads marketing tags. Moreover, if you are using heatmap tracking tools, you would need to integrate their tracking tags as well. That large number of tracking tags will definitely slow down your website if inserted directly into your source code.
What google tag manager does, however, is stop all the tracking codes from being placed on your website and replace them with the gtm container code. The data generated by your website is then transferred to your google tag manager account to be processed and sent to all third-party tools. That way, your website will have to load only one tag and the rest of the processing will be left to google tag manager.
Google recommends using its tag manager account for improving your website loading speed, which is a major SEO criterion.
Make it easier to manage and edit multiple tags from one web-based interface
By using Google tag manager, you can speed up the process of creating new tags at any time you might need them. Not just that, but if we had a penny for every time we needed to edit tags and couldn’t do it as we had to wait for the developer to finalize his everlasting pipeline!
Now marketers can use google tag manager to hasten that process and handle all code changes in a matter of a few minutes.
Tag Manager helps you debug tracking codes
With google tag assistant you can easily preview and debug all your tracking codes before publishing your container. This helps you identify any errors within your gtm account before making them live and saves you the trouble of your website going down.
Most common uses for Google tag manager
Digital Marketers and Data Analysts can use Google Tag Manager for many cases with different website types according to their objectives. Of course, Google Analytics’ basic events tracking is among the most common use cases for all website types. But, other than that, each website will a unique structure when it starts to manage tags.
and among those use cases are:
E-commerce website conversion tracking
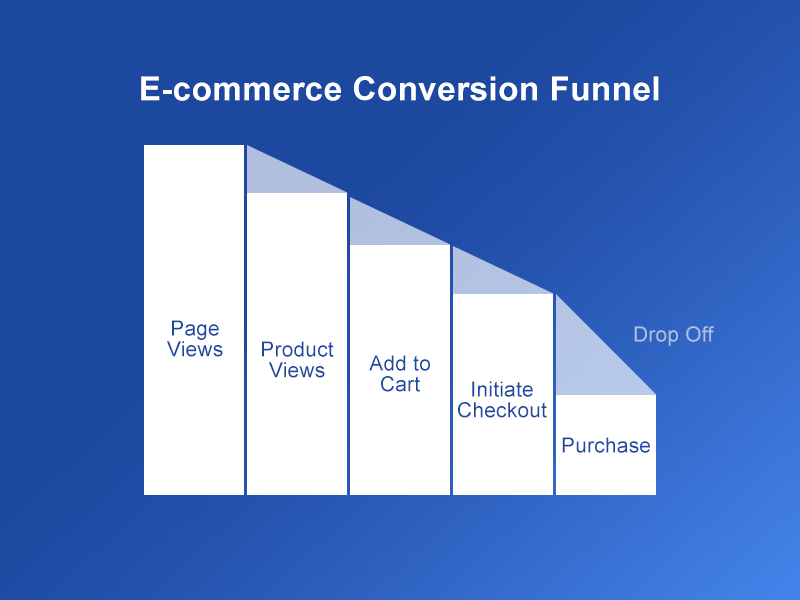
For e-commerce websites, there are a set of google tags and Meta standard events tags required for building effective marketing campaigns.
If you are marketing for an e-commerce website you will need to collect information regarding the entire process of user conversion. Your Google Analytics reports should provide you with the following events:
Page views
Product Views
Product Add to Cart
Product Remove from Cart
Checkout events
Purchase events
refund events
you will also need to set up Meta pixel standard events which are mostly similar to the above-listed one.
Blog website conversion tracking
The types of conversions for blogs are totally different from that of e-commerce websites. For example, when considering setting up google analytics reports for a blog post, you will consider the following events:
Time spent on each Blog post
Scroll depth
Outbound link clicks
e-books file downloads
Contact form submissions
user clicks on internal links
pdf downloads
Common questions about Google tag manager
How much is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is totally free for any number of accounts, containers, and users. you will even find free custom templates for implementing tags, triggers, and variables.
What is the difference between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics?
Google tag manager is a data collection tool, that works as an intermediary between your site and third-party tracking tools. Tag manager has nothing to do with data analyzing and reporting. Its only role is to extract information from your site and transform it into data blocks readable by Google Analytics and other third-party analysis tools.
Google Analytics, however, is responsible for analyzing the data received from Google Tag Manager and displaying it in the form of easily readable information by marketers and data analysts. Google Analytics has nothing to do with tag management.
Summing it all up
Google tag manager helps in managing all the tags needed for tracking or advertising your website. No matter how many tags you need for driving the best-customized reports, your website will never go slow. Google tag manager works as a container for all the tracking and advertising tags you might need. It then injects your website with every tag you created inside your tag manager container, but code loading doesn’t become the responsibility of the user’s browser.
Tag manager has three main parts, tags, triggers, and variables. Tags are the parts of the code that determine when a user takes an event on a given site. triggers are the functional parts of the code that fire tags when a user takes an action on the website. And variables store the different values that accompany each specific event.
Google tag manager is different from Google Analytics, as gtm is responsible for passing the data only to google analytics, while GA is responsible for analyzing and reporting the data.
If you have any questions regarding Google tag manager please leave them in the comments below or through an email, and please subscribe to our mailing list, so you can get an e-mail whenever we publish new articles that will definitely be of great help to you!




